Evaluation of the Thermogravimetric Profile of Hybrid Cellulose Acetate Membranes using Machine Learning Approaches
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14295/vetor.v33i1.15167Keywords:
cellulose acetate membranes, machine learning, Thermogravimetric analysis (TG)Abstract
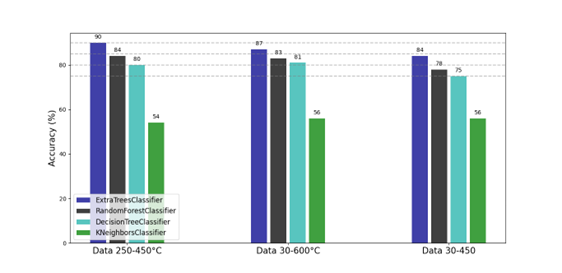
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is a characterization technique routinely used in materials science. In this particular case, TGA determines the variation of weight with temperature. The thermogravimetric analysis of cellulose acetate (CA) hybrid membranes can provide similar results, despite their different chemical composition. The present study uses machine learning algorithms to correlate data from thermogravimetric analyses with variations in chemical composition. Experimental points relating to temperature and weight from these analyses were treated in different ways and used to estimate the composition of the membranes. The Extra-Trees Classifier, Random Forest, Decision Tree, and K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithms were applied to this data and then evaluated using a confusion and accuracy matrix. The decision tree-based algorithms demonstrated a superior capacity for estimating the composition, albeit with negligible disparities in the thermogravimetric profile. The Extra-Trees Classifier algorithm, in particular, stood out for its ability to estimate composition in all tests, achieving 90% accuracy.
Downloads
References
I. H. Sarker, “Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions,” SN Computer Science, vol. 2, no. 3, paper no. 160, 2021. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00592-x
D. Morgan and R. Jacobs, “Opportunities and challenges for machine learning in materials science,” Annual Review of Materials Research, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 71-103, 2020. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurevmatsci-070218-010015
C. L. Ritt, T. Stassin, D. M. Davenport, R. M. DuChanois, I. Nulens, Z. Yang, A. Ben-Zvi, N. Segev-Mark, M. Elimelech, C. Y. Tang, G. Z. Ramon, I. F. J. Vankelecom, R. Verbeke, “The open membrane database: Synthesis–structure–performance relationships of reverse osmosis membranes,” Journal of Membrane Science, vol. 641, paper no. 119927, 2022. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119927
Y.-J. Hu, G. Zhao, M. Zhang, B. Bin, T. Del Rose, Q. Zhao, Q. Zu, Y. Chen, X. Sun, M. de Jong, and Q. Liang, “Predicting densities and elastic moduli of SiO2-based glasses by machine learning,” Npj Computational Materials, vol. 6, paper no. 25, 2020. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-020-0291-z
H. Khakurel, M. F. N. Taufique, A. Roy, G. Balasubramanian, G. Ouyang, J. Cui, D. D. Johnson, and R. Devanathan, “Machine learning assisted prediction of the Young’s modulus of compositionally complex alloys,” Scientific Reports, vol. 11, paper no. 17149, 2021. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96507-0
K. Low, R. Kobayashi, and E. I. Izgorodina, “The effect of descriptor choice in machine learning models for ionic liquid melting point prediction,” The Journal of Chemical Physics, vol. 153, no. 10, paper no. 104101, 2020. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0016289
M. C. Andrade, J. C. Pereira, N. de Almeida, P. Marques, M. Faria, and M. C. Gonçalves, “Improving hydraulic permeability, mechanical properties, and chemical functionality of cellulose acetate-based membranes by copolymerization with tetraethyl orthosilicate and 3-(aminopropyl) triethoxysilane,” Carbohydrate Polymers, vol. 261, paper no. 117813, 2021. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117813
V. Vatanpour, M. E. Pasaoglu, H. Barzegar, O. O. Teber, R. Kaya, M. Bastug, A. Khataee, I. Koyuncu, “Cellulose acetate in fabrication of polymeric membranes: A review,” Chemosphere, vol. 295, paper no. 133914, 2022. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133914
G. M. Ferreira, “Production and characterization of hybrid cellulose acetate membranes,” Master’s thesis, Materials Science and Technology Postgraduate Program, State University of Rio de Janeiro, Nova Friburgo, Brazil, 2022. Available at: http://www.bdtd.uerj.br/handle/1/17895
G. M. Ferreira, D. H. da Silva, K. C. Da Silveira, M. C. Gonçalves, and M. C. Andrade, “Evaluation of Thermal Degradation Kinetics of Hybrid Cellulose Acetate Membranes using Isoconversional Methods,” VETOR - Revista de Ciências Exatas e Engenharias, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 52-61, 2022. Available at: https://doi.org/10.14295/vetor.v32i1.13766
N. M. Abdulkareem and A. M. Abdulazeez, “Machine learning classification based on Radom Forest Algorithm: A review,” International Journal of Science and Business, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 128-142, 2021. Available at: https://ijsab.com/wp-content/uploads/676.pdf
F. Pedregosa, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, V. Michel, B. Thirion, O. Grisel, M. Blondel, P. Prettenhofer, R. Weiss, V. Dubourg, J. Vanderplas, A. Passos, D. Cournapeau, M. Brucher, M. Perrot, E. Duchesnay, “Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python,” Journal of Machine Learning Research, vol. 12, pp. 2825-2830, 2011. Available at: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/
B. T. Jijo, and A. M. Abdulazeez, “Classification based on decision tree algorithm for machine learning,” Journal of Applied Science and Technology Trends, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 20-28, 2021. Available at: https://www.jastt.org/index.php/jasttpath/article/download/65/24
H. A. A. Alfeilat, A. B. A. Hassanat, O. Lasassmeh, A. S. Tarawneh, M. B. Alhasanat, H. S. E. Salman, and V. B. S. Prasath, “Effects of distance measure choice on k-nearest neighbor classifier performance: A review,” Big Data, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 221-248, 2019. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1089/big.2018.0175